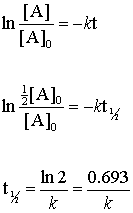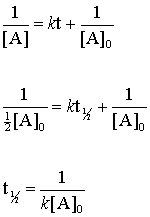half life formula for zero order reaction
Uses Of Zero Order Reaction. For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t12 0693k.

Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Class 12 Iit Jee Main Advanced Neet Aipmt Askiitians Youtube
Well here y is A the reactant concentration.
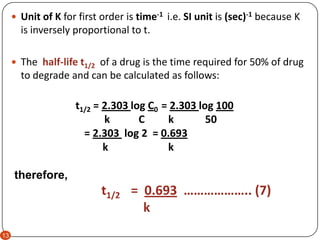
. NA Product The rate law of zero order kinetics is. The energy of activation for. The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k.
Remember from grade 9 how ymxb is the equation of a line. From the above-integrated equation we have. In a second-order reaction the half-life of the reaction is inversely proportional to the.
K t 12 12 A 0. By definition the half-life of any of the reactions is the amount of time the reactants take to consume half of the starting material. Where A 0 Initial concentration of reactant at timet 0.
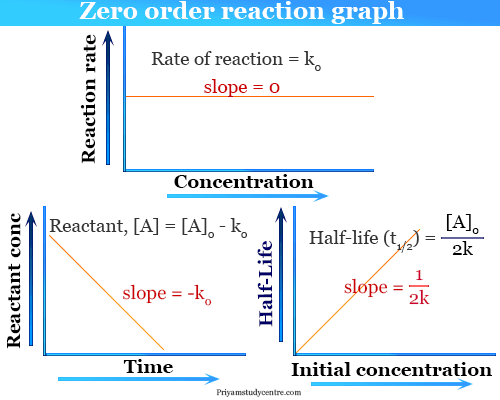
Which is the required equation for the half-life of zero order reactions. The half-life of a reaction is referred to as t 12 unit - seconds The initial reactant concentration is referred to as R 0. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R02k.
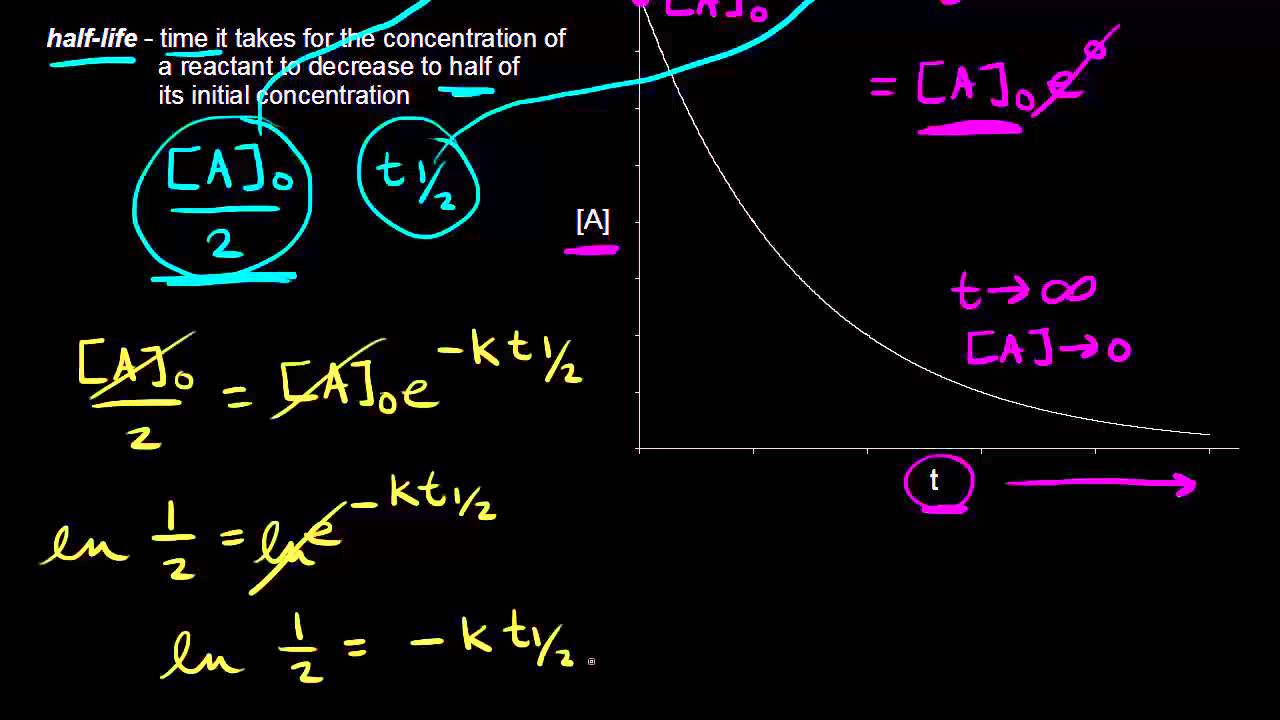
When t t ½ C C o 2 and the equation 87 becomes. If the reaction is zero-order a graph of A vs. The half-life of a Zero-th order reaction is t A0 2kHere I derive this from the Integrated Rate LawAsk me questions.
Because this equation has the form y mx b a plot of the concentration of A as a function of time yields a straight line. Where a is initial concentration of reactants. A A 0 - kt.
If we know the integrated rate laws we can determine the half-lives for first- second- and zero-order reactions. The half-life formula for various reactions is given below. A zero order reaction implies that the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of the reactant.
The rate constant for the reaction can be determined from the slope of the line which is equal to -k. And for the second-order reaction the formula for the half-life of the reaction is given. For a zero order reaction Half life decreases with decreasing concentration For a 1st order reaction Half life is constant For a second order reaction Half life increases.
Then injection of maximum activity of radioactive substance that can be injected will be Answer. Now replacing t with half-life t12 in the above equation. For a general reaction.
Not a set value that we can calculate. The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k. In a reversible reaction the energy of activation of the forward reaction is 50 kcal.
T will give a line. In this video We will cover-- Integrated Rate expression and Half life of a reaction for zero order ReactionOur previous Video links-Chemical kinetics Par. 12 A A 0 - k t 12.
The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR 0. For this discussion we will focus on reactions with a single reactant. Half-life of radioactive substance is 6 h.
T 12 A 0 2k. The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR 0. Thus for t t 12 A t ½ A o.
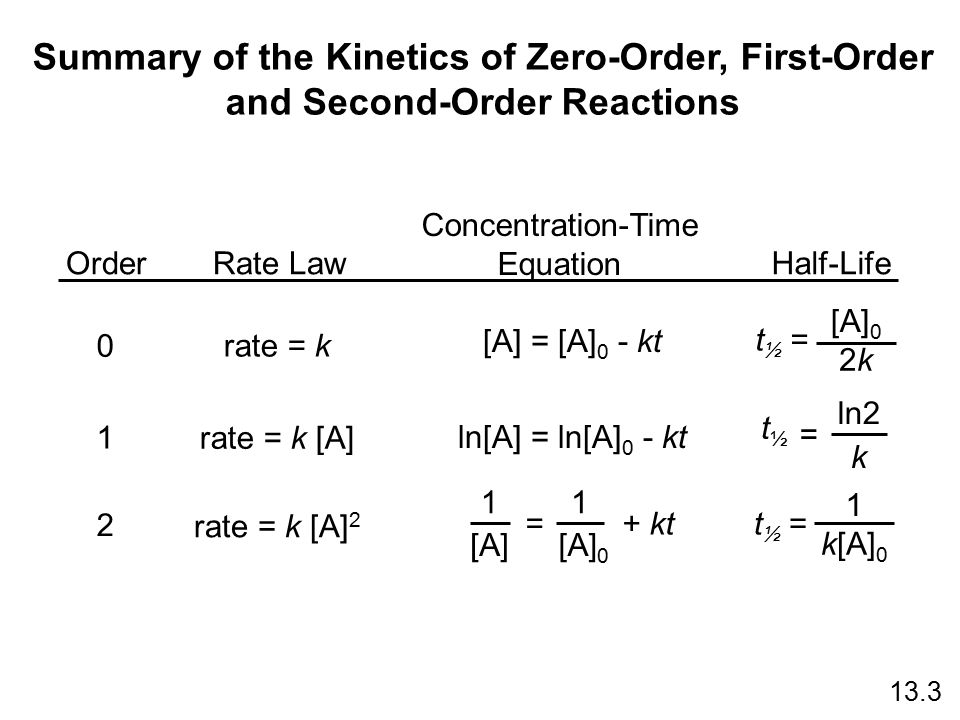
The integrated rate constant for the zero-order reaction is given by. The formula for the half-life of different reactions is given below. It is to be noted that the formula for the half-life of a reaction varies with the order of the reaction.
Unlike a first-order reaction in a zero- or second-order reaction the half-life is dependent on the initial concentration ie. The half-life for zero-order and second-order reactions half-life changes based on the concentration of the reactant. Half life of zero order reaction is directly proportional to the initial concentration of reactants.
The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t12 R 02k. Order reaction from a plot of A versus t by the variation in the time it takes the concentration of a reactant to change by half. The integrated rate law for the zero-order reaction A products is A_t -kt A_0.
The reaction of hydrogen with chlorine also known as a photochemical reaction is of zero order. Equation 89 shows that the t ½ of a zero-order process is not constant but proportional to the initial concentration of drug C o and inversely proportional to the. And we typically use the concept of half-life to for example determine the age of ancient artifacts or predict when a radioactive sample will be safe to handle.
M the slope is -k and b the y-intercept where t0. The equation given above shows that the half-life is dependent on the rate constant and the reactants initial concentration cell. Half-life of a first.
The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R 0 2k. X is t the time elapsed. This is an expression of the half-life of a zero-order reaction.
We can identify a 0 1 st or 2 nd. T 12 12 k A 0. The half-life is the time required for a quantity to fall to half its initial value as measured at the beginning of the time period.
Correct option is A Half life of zero order reaction is given by t 21 2ka. The half-life of a reaction is defined as the time required for the reactant concentration to fall to one half of its initial value. Half life formula for nth order reaction.
T 12 is the half-life of. Half-life t ½ or half-time is defined as the time period required for the concentration of drug to decrease by one-half. 1A n-1 1 A 0 n-1 n-1 kt.
First Order Reaction Derivation And It S Half Life Time Chemical Kinetics Chapter Youtube

Zero Order Reactions Video Kinetics Khan Academy

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube

Integrated Rate Laws Zero First Second Order Reactions Chemical Kinetics Youtube
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula
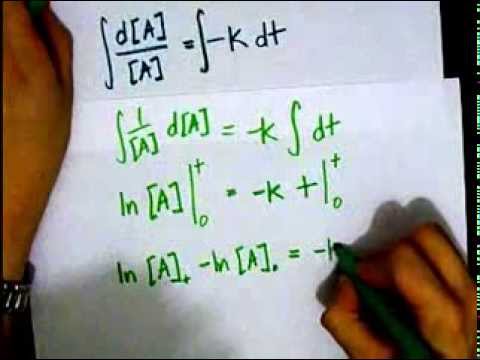
Integrated Rate Law First Order Reaction Youtube
Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
Summary Of The Kinetics Of Zero Order First Order Ppt Download
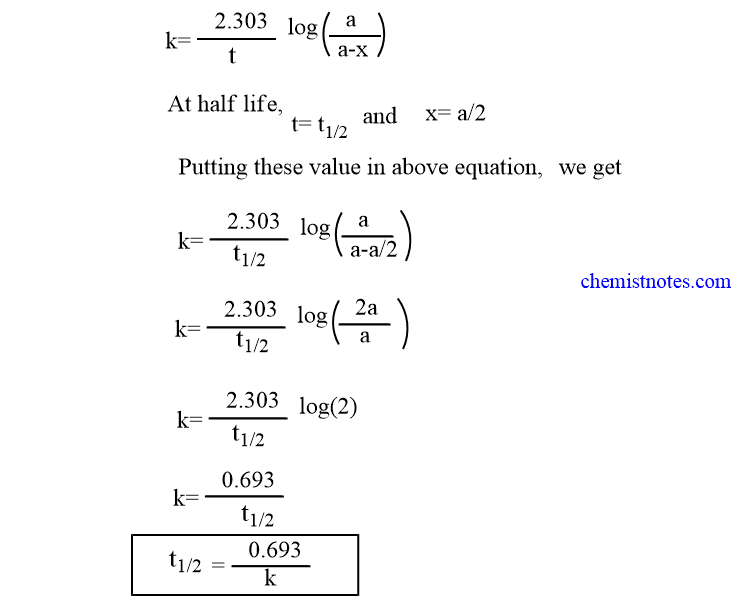
First Order Reaction Definition Example Half Life Period Chemist Notes

How To Find The Rate Constant For A Zero Order Reaction From A Graph Youtube

Half Life Of A Zero Order Reaction Is 250sec T75 T100 Of The Reaction Respectively In Sec Are Edurev Neet Question